Diabetic foot infections: Prevention and Treatment
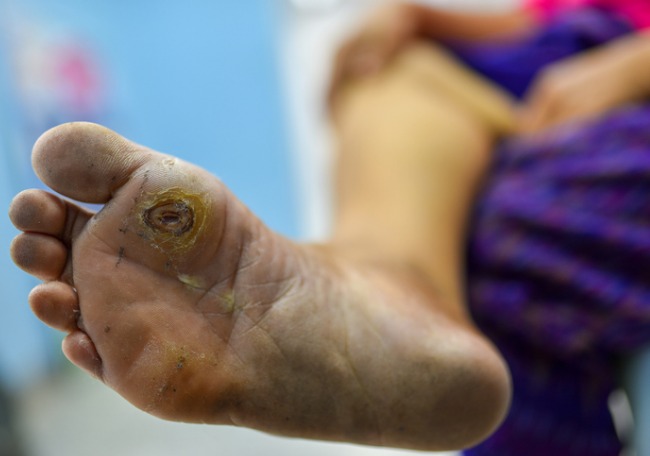
Diabetic foot infections are associated with serious complications and are the leading cause of diabetes-related hospitalization and lower limb amputation.
Diabetic foot is defined by the WHO as ulceration, infection or gangrene of the foot. It is associated with diabetic neuropathy and peripheral arterial disease, and is the result of the complex interaction of different factors, mainly metabolic.
Between 19 and 34% of patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) have a foot ulcer in their lifetime and between 14 and 24% of these patients require amputation.
After a major amputation, patient survival decreases by up to 50% at 5 years, which implies a higher mortality than that of several types of cancer.
The germs involved in diabetic foot infection vary according to the characteristics and the time of evolution of the lesion, the place of residence of the patient and the previous use of antibiotics, among other factors.
- In ulcers without infection, antibiotic treatment is not recommended.
- In clinically infected lesions, it is recommended to take a sample for culture and the initiation of empirical antibiotic treatment in order to avoid the progression of tissue damage while waiting for the identification of the infectious agent.
Table of Contents
What can I do to prevent diabetic foot infections?
The diabetes is the most common cause of amputation of the foot in developed countries and it is estimated that the number of patients’ diagnosed diabetes will increase significantly.
Many of these amputations could be avoided, to the extent possible, if the necessary preventive actions were taken. Here are a series of tips:
1. Perform neuropathy and vasculopathy screening
It is recommended to perform neuropathy and vasculopathy screening once a year to check the status and evolution of the disease. It should be noted that, in patients at risk, it is advisable to do it in every six months.
2. Observe the foot daily
It is advisable that every day we carefully observe the feet paying special attention to the tip of the big toe, the rest of the toes, especially on the bottom, the heel and the sole, without forgetting the outer area of the foot.
If we see that there is any abrasion, wound or redness, the ideal thing is to go to a specialist because, as they say, “prevention is better than cure”.
3. Be careful when cutting nails
The cut must be straight using a nail clipper, and trying never to leave corners as this can cause an injury to the skin. In patients with diabetes, a small wound that we could not give importance to can be the starting point of a possible infection. Therefore, we advise you to go to the podiatrist if necessary to avoid these types of problems. It may seem banal but it is not.
4. Pay special attention to hygiene
In a diabetic patient it is important to wash the feet every day and keep them very clean. It is advisable to do it with warm water and soap.
It should be remembered that many patients do not have sensitivity in this part of the body and not feeling the water too hot can cause a burn. For this reason, we will also have to avoid heating the feet with water bags or placing them near stoves and radiators.
Drying your feet well will also be essential, as well as hydrating them with specific creams, caring for them to avoid the appearance of calluses or corns or applying powders if they sweat excessively.
5. A quality footwear with synthetic socks
The best shoes are leather ones. It is advisable to check inside every day as a small stone, for example, can cause a wound.
Thus, extreme precautions must be taken with regard to footwear. Next, we detail the most relevant aspects in terms of its characteristics:
- Choose a shoe that does not oppress or loose fit and is lightweight.
- Numbering based on forefoot width.
- The shovel must be wide and high.
- The interior must not have seams.
- The sole must be rubber and non-slip.
- The heel should be 2 or 3 centimeters.
- Lace-up or velcro footwear.
- Semi-rigid buttress.
- The materials of the shoe must be breathable like leather.
If we have new shoes or sneakers, we must try to wear them in the afternoon and less than an hour a day. In addition, at home you do not have to walk barefoot but with comfortable slippers. Neither for swimming pools or beaches.
On the other hand, socks will also play a prominent role. We recommend diabetic socks which will be synthetic, without large seams and that they do not squeeze since this way the blood will circulate better.
Prevention of diabetic foot infection
In addition to the advice set out above, to prevent short and long-term problems it is advisable to carry out a neuropathic and vascular study, which is what perform on diabetic patients.
Different tests are carried out in order to determine the degree of affectation in the sensitivity of the foot and the degree of blood supply. Some of the tests are as follows:
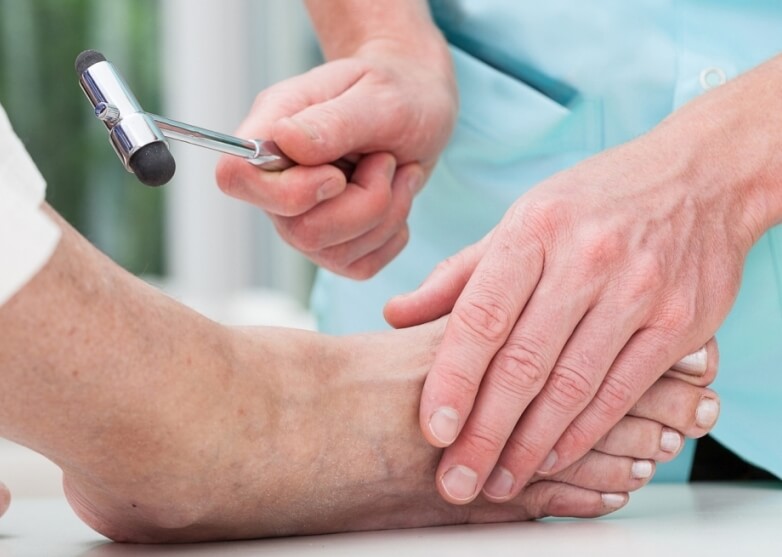
1. Examination of sensation (diabetic neuropathy)
Through the use of certain devices, the degree of affection of the sensitivity in the foot that the patient has is diagnosed. Both deep and superficial sensitivity are evaluated.
It is very important to detect a decrease in sensitivity (neuropathy) early to establish prevention plans that can avoid problems in the patient and to monitor the condition of neuropathy over time. Through a tuning fork and monofilament, deep or proprioceptive inspection is performed.
2. Vascular examination (diabetic vasculopathy)
This examination allows us to assess the status of the blood supply to the foot in order to be able to refer the patient to the vascular doctor in the necessary cases. It is done using a device called a Doppler.
3. Barapodometric study
It helps us to predict what may happen (appearance of an ulcer, injury and even amputation) by obtaining the static and dynamic analysis of the plantar pressures of the patient and diagnosing potential problems derived from excess pressure in certain areas of the foot sole.
Treatment for diabetic foot infection
If we know that the main cause of ulceration is the pressure maintained in a specific point of the foot and if we are able to detect those pressure points before the ulcer forms, by means of a personalized insole we will be able to eliminate overload points, minimizing greatly measure the risk of ulceration.
For all this, we obtain a virtual mold of the foot with total precision. Subsequently, the insole is manufactured in a robotized way, using specific materials that allow us to eliminate the overload points detected in the foot. What do we get?
- Redistribution of pressures
- Containment of deformities
- Compensation for biometric alterations
It is important to understand that having diabetes should not be directly related to suffering from ulcerations or amputations on the feet, far from it. The important thing is to understand that the feet are a sensitive part in this type of patient and that it is convenient to carry out the appropriate reviews with the appropriate means to be able to carry out all those preventive actions necessary to avoid any complications. If a wound appears even minimal, we must not doubt, we must go to a consultation.
In short, our advice is to go periodically to the podiatrist to perform the inspection and care of the foot (correct nail cutting, callus delamination, heloma treatments, etc.) and once a year repeat the neuropathic and vascular study to be able to assess the evolution of the possible vasculopathy and neuropathy to carry out the necessary preventive actions.