Sarcoidosis: Symptoms and Treatment
Included within the family of rare diseases, sarcoidosis is a disease that can affect any organ. What are its symptoms or warning signs? Is there a definitive treatment? These are some of the questions that will be answered in order to know a little better what is behind the diagnosis of sarcoidosis.
Sarcoidosis is absolutely not a contagious disease. The main concern of those who suffer is that, today, no cure, but there are treatments to combat and delay its progression. Sarcoidosis is a disease caused by abnormal swelling of the tissues of an organ, which may affect proper operation. It can affect one or more organs while being located mainly in the lungs, skin, heart, lymph nodes, liver, eyes, nerves or brain.
Table of Contents
Sarcoidosis: symptoms
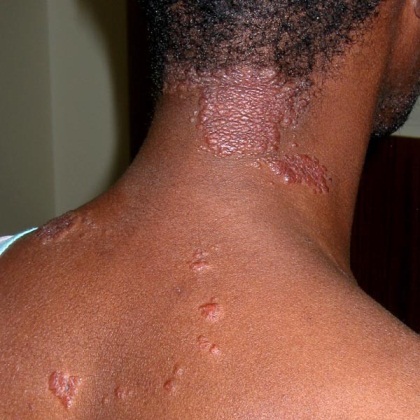
The most common symptoms of sarcoidosis (recognized as a rare disease) are series of fever, ulcers in the skin, and shortness of breath, joint pain, chest pain, fatigue, dry cough and weight loss. Symptoms that logically depend on the affected organ.
It is unknown origin, although it is possible that there may be a strong genetic component in onset, causing an abnormal immune system response. Similarly, sarcoidosis has a fixed pattern, since in some cases can flare up in a few weeks and show obvious symptoms. In others, it may be asymptomatic in its early stages and evolve slowly over months or even years. When suddenly appears treatment is usually more effective, making the symptoms subside. In the second case, the patient is at risk of the disease to become chronic.
Sarcoidosis: Diagnosis
Diagnose sarcoidosis is important to apply the appropriate treatment, especially if it is affecting the functioning of an organ. In addition to the physical examination of the patient, other specific tests to determine the target organ (eg an X-ray when it is suspected from the symptoms of pulmonary sarcoidosis), and a review of medical records was also performed and family of the patient.
Sarcoidosis: Treatment
Sarcoidosis not always requires treatment, and sometimes refers to as appeared. However, the physician must determine whether it is necessary or not to administer certain drugs. Similarly, when talking about drugs, we should remember that we must make responsible use of them, that is, follow your doctor’s instructions for treatment to be effective (dose, duration).
Currently available treatments can relieve symptoms and slow its evolution. In some cases, in addition to treating inflammation, you also have to reduce injuries in the affected organ. The drugs most frequently used in the treatment of sarcoidosis are corticosteroids (prednisone, the most common), Methotrexate (generally used in combination with the most drugs are immunosuppressants. But you must first concern with your doctor before taking any medicine. It is advisable to accompany treatment with proper diet and that will help to strengthen our defenses. In the case of sarcoidosis, especially lung, you must leave the snuff.