3 Most Common Oral Hygiene Problems
There is more to preserving your teeth than correct brushing and flossing. Sometimes, in spite of our best efforts, we still get cavities or suffer from gum disease. In fact, the latter is more of a problem than most of us realize: gum disease is by far the biggest cause of tooth loss in adults.
Cleaning your teeth properly plays a huge part in preventing problems such as cavities or gum disease, but it’s not always enough.
Other factors like diet, lifestyle, and even your genetic makeup all play a role in the state of your teeth and gums. Also, generally speaking, children and adults fall into different risk groups.
Because you can’t guarantee perfect oral health through your own efforts alone, you need to visit your dentist every six months. You must be aware that there are more serious oral conditions than cavities such as cancer that will require professional dental treatment. Report any changes you see or feel in your mouth to your dentist as soon as you notice them.
Table of Contents
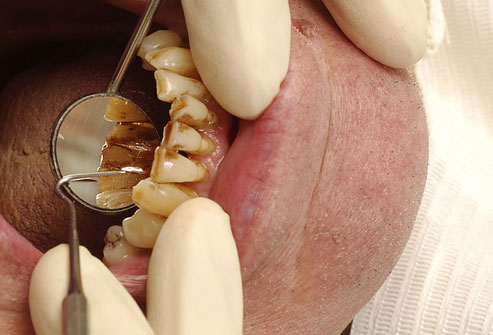
Tooth Decay
Tooth decay, or dental caries, has been around for centuries. It’s also the most common disease in the world today. Decay poses the biggest threat to children’s teeth, but that doesn’t mean that adults are exempt.
To understand tooth decay, you must understand plaque: a combination of saliva, food particles, and oral bacteria in the mouth that sticks to the teeth. All three factors have to be present for plaque to form, but they only take a few hours to accumulate. Once plaque starts to form, the bacteria produces organic acids that eat away at the hard tissue of the tooth, and you have the beginnings of a cavity.
Once the acids start to decalcify the surface of the tooth, the enamel in the area becomes softer and chalk-white in color. This is the first sign of tooth decay.
Minimize your risk for teeth decay
Cut down the number of times you eat carbohydrates each day. Eating carbohydrates less often means there is less acid in contact with your teeth, and therefore, fewer occurrences of cavities. As a guideline, the stickier the food, the worst it is for your teeth.
Gum Disease
Gum disease is the major cause of tooth loss in adults over 35 years old and it does so much more often than tooth decay. About 80 percent of tooth loss in this age group can be credited to gum disease. A lot pain and suffering could be avoided by catching it and treating it early.
Gum disease affects the supporting structures of the teeth, which are the gums, bone, and ligaments. It is a long-term disease that moves slow. It starts off being painless, but later it develops a chronic inflammation that negatively affects the gums and the bone holding the teeth in place.
Bacterial plaque is the biggest cause here, and when it is not properly removed, its millions of bacterial organisms combine with saliva to form a hard porous deposit called tartar.
Treat for gum disease
Pay attention to the health of your gums on a daily basis and visit your dentist if you notice any changes. While plaque is the main cause of gum disease, there are other factors to consider, all of which affect the health of your gums: diet, smoking, stress, medication, and pregnancy.
Abscesses
Dental abscesses happen for many different reasons and you may not always know one is present because while acute abscesses are painful, chronic abscesses are not.
Acute abscesses hurt because the abscess causes swelling and there isn’t any room anywhere around the tooth to accommodate that swelling. Swelling is normal when there is an infection inside the body because of fluid buildup in the area.
Sometimes that fluid has nowhere to go, and the result is pain. Chronic abscesses tend to not hurt because the fluid has found a way to escape, which allows it to drain and relieve pressure, thus you won’t feel any pain.
Abscesses Treatment
Dentists treat abscesses several different ways depending on what it has affected and where it is located. The ultimate goal is to rid the source of the infection and drain the abscess. This can be done by root-canal treatment, periodontal reparation, tooth extraction, or use of antibiotics.