Cutaneous Xerosis causes and treatment
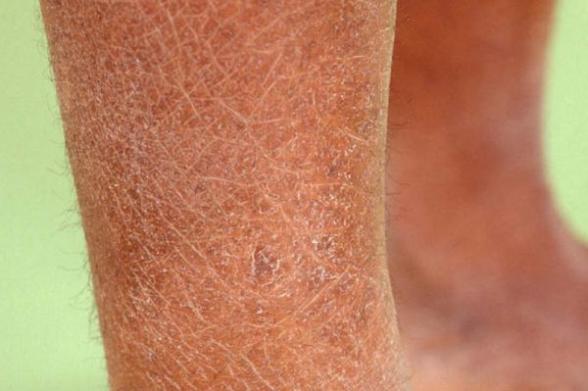
Xerosis is a term used to refer to a skin condition in which there is an abnormal dryness, characterized by a rough, desquamative and usually pruritic skin, that is, with itching. This condition has a high prevalence in the general population. The Xerosis skin is not necessarily a disease, it can be due simply to some environmental conditions, because in extreme conditions, the skin can become so weak that cracks can start to appear.
This condition is called crackle eczema, a skin disorder that, in addition to desquamation, is characterized by intense itching. In the following article we inform you more about this condition; cutaneous xerosis: treatment, causes and conditioning factors.
Table of Contents
What is cutaneous xerosis
The skin consists mainly of two layers: the epidermis and the dermis, the epidermis in turn has multiple layers of cells that give the skin necessary protection – the number of cell layers gives the thickness of the skin of each part of the body, these cells are constantly changing to provide a better protective effect.
In addition, in the most superficial layer is an additional layer of proteins, lipids and water that gives more firmness to the skin, this layer is called stratum corneum, and the decrease in the water content of this area is the cause of the cutaneous xerosis. Dehydration occurs when there is an imbalance between the normal loss of water and the contribution.
The ability of the skin to regulate the amount of water is given by the following mechanisms:
- Multiple molecules in such as urea, lactate, PCA (pyrrolidone carboxylic acid), salts or some amino acids, have the function of attracting and retaining water.
- The effectiveness of skin lipids, such as ceramide, have the function of reducing the loss of water by evaporation.
Conditioning factors
Some factors can influence the appearance of cutaneous xerosis, among which are:
- Inheritance, the children of parents who suffer from Cutaneous Xerosis have a higher risk of suffering from this condition.
- Age.
- Some environmental conditions can influence the structure and function of the skin, for example winter can decrease some lipids that are in this layer, low humidity, or solar radiation.
- Some chemical agents such as detergents, lotions, perfumes or drugs may increase the risk of presenting Xerosis cutis.
Some diseases can increase the risk of having cutaneous xerosis, among which are:
- Atopic dermatitis
- Allergic rhinitis
- Asthma
- Urticaria
- Psoriasis
- Hypothyroidism
- Intestinal absorption deficits.
Xerosis causes
The causes of xerosis are the lack of certain elements responsible for nourishing and protecting our skin. Here we explain them:
Deficiency in the lipid skin barrier: The epidermal lipids are responsible for attaching the cells in the superficial layers of the skin, moreover, are responsible for creating a protective barrier and retain moisturizing elements; its deficiency is associated with dry skin, rigid and rough.
Deficiency in natural factors of hydration (MFN): Along with urea, the natural factors of hydration, such as Pyrrolidine Carboxylic Acid, salts and sugars, are responsible for attracting moisture and retain it in the most superficial layer of the skin, the stratum corneum, which prevents dehydration, peeling and deterioration.
Natural treatment for Xerosis
The basis of the treatment is to restore the barrier, rehydrating it and externally placing some of the components that are normally found, such as lipids. Small changes in our lifestyle can be very beneficial for this condition:
- Drink enough water.
- Follow a balanced and varied diet ensuring the consumption of fruits and vegetables.
- Adding salt to bath water is an effective measure to reduce xerosis and itching.
- Avoid the consumption of alcohol, tobacco and photoexposure.
- Avoid direct contact with irritants.
- Do moderate regular exercise.
- Use soaps for daily hygiene with moisturizers and acid pH.
- After bathing with warm water, immediately apply products that prevent the evaporation of water contained in the skin.
- Avoid friction of the skin with sponges or bath gloves.
- Use specific soaps that are not irritating.
- Do not use lotions, colognes, perfumes or similar with alcohol content.
- Use soft clothing in contact with the skin, preferably cotton.
- Avoid wearing tight clothing, the combination of physical aggression (friction) with compression, can limit blood circulation and, consequently, the correct supply of oxygen and nutrients.
If you have this condition for a long time, we recommend that visit your doctor to prescribe a topical solution and tell you what the best creams are for xerosis skin to recover lipids and normal hydration of the skin.