What is alopecia areata and how is it treated?
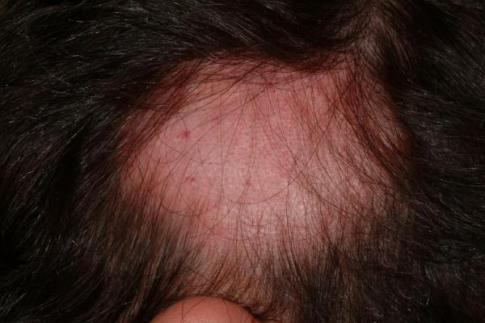
Alopecia areata, which can affect both men and women and at any age, is an autoimmune disease that affects the hair follicles. The most visible symptom is fall of the hair to tufts, leaving bald spots or patches on the scalp.
In severe chaos, hair loss can be total, not only in the head but also in other body areas. Why this hair loss? What are the most common causes? What is the best treatment? Alopecia areata is not only physical, but also psychological consequences, as it directly affects our image.
Table of Contents
Alopecia areata causes
There is no specific cause to explain the onset of alopecia areata. The researchers point to the influence of genes that predispose us to a greater or lesser extent to suffer from this disorder. In fact, according to medical data, it is estimated that one in five people with alopecia have a family history of the same disorder.
While there are several risk factors that can act as a trigger, such as unbalanced diets, stress episodes, various infections, problems of thyroid or an excess of vitamin A. In the case of women there is another factor to take into account, and the fall in production of hormones during menopause or after a complicated delivery.
Alopecia areata symptoms
Hair loss is the most obvious symptom and sometimes the only one that reveals a condition of alopecia areata in the scalp. In some cases, however, other symptoms may occur, such as itching or irritation of the scalp. The appearance of one or more patches or clear round on the scalp usually mark the beginning of alopecia areata. The alopecia can be a whole, when the hair of the head gets lost, or universally, when it gets lost of the whole body.
Treatment for Alopecia areata
Currently, there is no definitive treatment for alopecia areata, but there are therapies and medicines that help stop the hair loss and stimulate hair follicles that are dormant.
Among the available treatments, cortisone injections are the most effective treatment when the alopecia does not affect the entire scalp, as well as steroid creams. In the case of extensive alopecia, treatment is usually more complicated. Among the options, oral steroids, treatment with UV rays called PUVA or Anthralin or Cyclosporine creams.