Angioma: What is it, what are its symptoms and how is it treated?
An angioma or hemangioma is a benign tumor formed from the cells of the blood vessels. The most common are at the surface level, forming spots on the skin.
However, angioma can develop from any blood vessel and form a mass. Hepatic hemangioma is relatively frequent.
Table of Contents
What is angioma?
The blood vessels are formed by several layers that form a light through which the blood circulates. There are different types of vessels depending on their size and length. The arteries are divided giving thinner vessels called arterioles. In turn, the division of the arterioles forms the capillaries.
Cutaneous angioma, which are the most frequent, develop from capillaries. These vessels are very thin and are the ones that reach the most superficial layers of the skin that is why they are visible.
They are usually present from birth or formed during the first year of life. The mechanism by which they are produced is not known exactly, it is believed to be an alteration in the formation of blood vessels. These proliferate abnormally forming reddish spots that we will explain below.
In the case of angioma that affect internal organs may involve arterioles or vessels of high caliber. The formation and renewal of blood vessels is disrupted and a mass is formed. In this case they usually appear in adulthood. Although they are not malignant, if they are of a considerable size, they can alter the function of the organ.
Angioma Symptoms
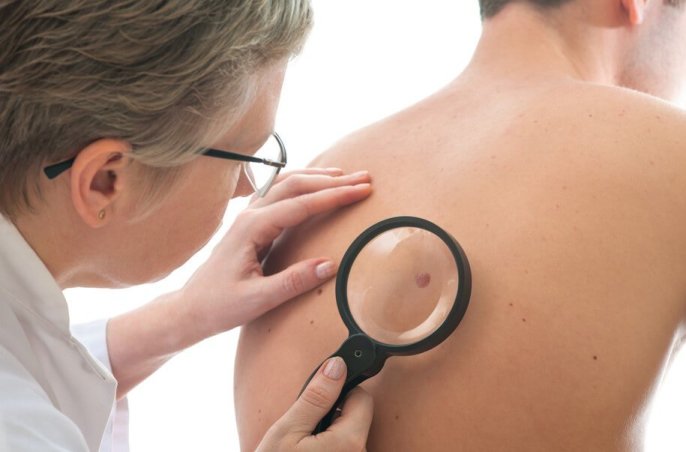
Cutaneous angiomas do not produce symptoms. They look like reddish spots located anywhere on the body. They are more frequent on the face, genitals and anus. Depending on the vessels that it affects, it can be more or less superficial.
There are many types of cutaneous angioma depending on their shape and location. They can range from large, deep red spots to small plates with an arboriform structure and a bluish color.
The infantile form present from birth usually grows during the first months of life. By the end of the year they can stabilize and sometimes disappear.
Angiomas that affect the vessels of the organs do not produce clinical symptoms either. In contrast, in this case they can interfere with the normal function of the affected organ. In these cases, surgical removal may be indicated.
Complications of angioma
Although they are benign entities that do not have to involve pathology, complications can arise. The main ones are:
- Ulceration: It is the most frequent complication, it appears in up to 10% of the angiomas. An open wound forms in the angioma that causes pain and may bleed. In addition, healing can leave scars.
- Infection: Occurs in some cutaneous angioma, mainly due to streptococcus pyogenes bacteria.
- Aesthetic problems: Sometimes the location or size of the tumor can interfere with the comfort of the subject. It occurs mainly in angiomas located in visible areas, such as the face or arms.
- Complications associated with localization: Depending on the place where the angioma is formed, it can interfere in different functions. They are very varied, from visual impairment if they are close to the eye and intervene with vision; even neurological complications if they are in the nervous system.
Diagnosis and treatment of angioma
Cutaneous angioma can be diagnosed by inspection and palpation of the lesions. In contrast, deep angiomas require imaging tests such as CAT scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
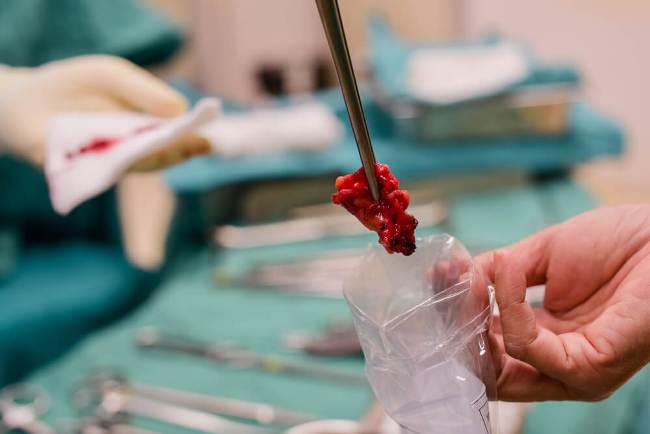
If there are doubts, a biopsy may be necessary, that is, extract a part of the lesion and then analyze it under a microscope. This test gives the confirmation diagnosis by allowing observing the cells of the blood vessels forming a mass.
The treatment of cutaneous angioma depends on the aesthetic repercussion and possible complications. Conservative treatment can be done by monitoring the evolution since, as we have said, sometimes they disappear. In addition, although they do not disappear, the lesions stabilize and do not continue to grow.
If the angioma increases in size or presents some complication, may be indicated the need for treatment. The options are several, from taking corticosteroids to laser application to eliminate it. One or the other therapy will be chosen according to the age of the patient, the location and the characteristics of the lesion.
Deep angioma should also be monitored, and if they alter the function of the organ it is indicated that they should be removed by surgery.